Sign in with Apple - SwiftUI, MVVM
Sign in with Apple is a new way to sign in to your app just like facebook and google with all apple privacy and security.
Sign in with Apple is the fast, easy, and more private way to sign in to third-party apps and websites using the Apple ID that you already have. Sign in with Apple is built from the ground up to secure your privacy and personal data. At your first sign-in, apps and website can ask only for your name and email address to set up an account for you.
You can also hide your personal email address from the app or website. if you choose to hide your personal email address then a unique, random email address is generated so your personal email address isn't shared with the app or website developer during the account setup and sign in process. This address is unique to you and the developer and follows this format: <unique-alphanumeric-string>@privaterelay.appleid.com
Let's implement Sign in with Apple using SwiftUI by following MVVM architecture.
- On the signing & capability pane, set the bundle id to unique identifier.
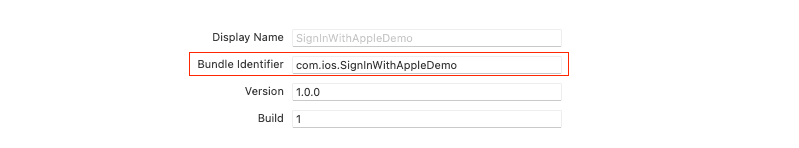
- Add your apple id account and assign the target to the team so Xcode can enable sign in with Apple in your provisioning profile. You can also add this capability on the apple developer portal manually.
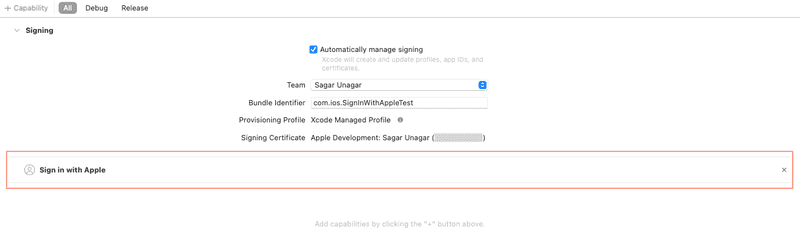
- Choose a run destination from the scheme pop-up menu that you're signed into with and apple id and that uses two factor authentication(TouchID or FaceID)
- If necessary, click register device in signing & capabilities to create the provisioning profile.
- In the toolbar, click run or choose Product > Run
Here is the project structure,

Add a Sign in with Apple button
We can add the Sign in with Apple button in our view by importing AuthenticationServices. Using this button we can create authorization requests with the scope and also handle the results.
SignInWithAppleButton(.signIn,
onRequest: { request in
request.requestedScopes = [.fullName, .email]
},
onCompletion: { result in
authenticationViewModel.didFinishAuthentication(result: result)
}
)In the above code snippet, Sign in with Apple button has three parameter as follows,
- label: This is the button title that displays title like Continue, Sign In or Sign up
- onRequest: Setup request and scope
- onCompletion: Handle the authorization result
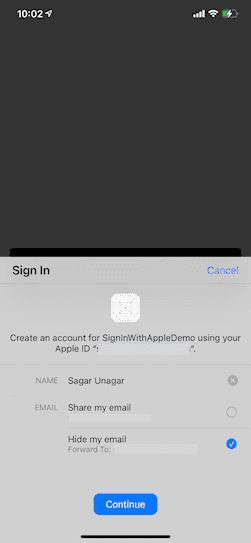
Handle authorization result
On completion of the request, we will get the authorization result whether the user successfully signed in or not.
func didFinishAuthentication(result: Result<ASAuthorization, Error>) {
switch result {
case .success(let authorization):
guard let credential = authorization.credential as? ASAuthorizationAppleIDCredential else {
shouldShowAlert = true
alertTitle = "Error"
alertMessage = "Something went wrong. Please try again later."
return
}
saveUserData(name: credential.fullName?.givenName, email: credential.email, userId: credential.user)
case .failure(let error):
shouldShowAlert = true
alertTitle = "Error"
alertMessage = error.localizedDescription
}
}If the user gets successfully signs in then store the user information in UserDefautls or Keychain and if it fails then show an alert to the user.
Revoke the permission and handle the changes
We can revoke the permission for the app from Settings > Apple Id > Password & Security > Apps using your Apple ID
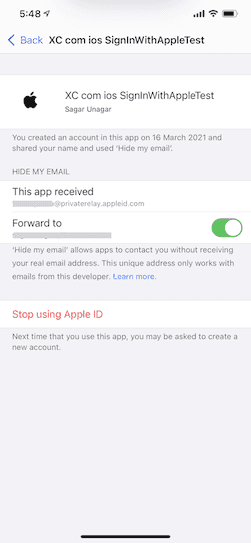
When we press "Stop Using Apple Id" we also need to handle that change in our app and we can handle it using ASAuthorizationAppleIDProvider.credentialRevokedNotification notification and we need to register for it in our ViewModel like this,
init() {
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(self, selector: #selector(getAuthorizationState), name: ASAuthorizationAppleIDProvider.credentialRevokedNotification, object: nil)
}@objc func getAuthorizationState() {
let provider = ASAuthorizationAppleIDProvider()
if let userId = UserDefaults.standard.value(forKey: "userId") as? String {
provider.getCredentialState(forUserID: userId) { [self] (state, error) in
switch state {
case .authorized:
// Credential are still valid
break
case .revoked:
//Credential is revoked. It is similar to Logout. Show login screen.
self.deleteUserData()
break
case .notFound:
//Credential was not found. Show login screen.
self.deleteUserData()
break
case .transferred:
//The app is transfeered from one development team to another development team. You need to login again so show login screen.
self.deleteUserData()
break
default:
break
}
}
}
}Code
SignInWithAppleDemoApp.swift
import SwiftUI
@main
struct SignInWithAppleDemoApp: App {
@ObservedObject var authenticationViewModel: AuthenticationViewModel = AuthenticationViewModel()
@AppStorage("email") var email: String = ""
init() {
authenticationViewModel.getAuthorizationState()
}
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
if email == "" {
AuthenticationView(authenticationViewModel: authenticationViewModel)
} else {
HomeView()
}
}
}
}HomeView.swift
import SwiftUI
struct HomeView: View {
@AppStorage("name") var name: String = ""
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("Hello \(name), Have a good day!")
.font(.title)
Spacer()
.frame(height: 100)
}
}
}AuthenticationView.swift
import SwiftUI
import AuthenticationServices
struct AuthenticationView: View {
@ObservedObject var authenticationViewModel: AuthenticationViewModel
var body: some View {
VStack {
SignInWithAppleButton(.signIn,
onRequest: { request in
request.requestedScopes = [.fullName, .email]
},
onCompletion: { result in
authenticationViewModel.didFinishAuthentication(result: result)
}
)
.scaledToFit()
.padding()
}
.alert(isPresented: $authenticationViewModel.shouldShowAlert, content: {
Alert(title: Text(authenticationViewModel.alertTitle), message: Text(authenticationViewModel.alertMessage), dismissButton: .default(Text("OK")))
})
}
}AuthenticationViewModel.swift
import Foundation
import AuthenticationServices
class AuthenticationViewModel: ObservableObject {
@Published var shouldShowAlert: Bool = false
@Published var alertTitle: String = ""
@Published var alertMessage: String = ""
//get notified when autherization state gets change
init() {
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(self, selector: #selector(getAuthorizationState), name: ASAuthorizationAppleIDProvider.credentialRevokedNotification, object: nil)
}
//handle the authorization result that returned from the authorization request in Sign In with Apple button
func didFinishAuthentication(result: Result<ASAuthorization, Error>) {
switch result {
case .success(let authorization):
guard let credential = authorization.credential as? ASAuthorizationAppleIDCredential else {
shouldShowAlert = true
alertTitle = "Error"
alertMessage = "Something went wrong. Please try again later."
return
}
saveUserData(name: credential.fullName?.givenName, email: credential.email, userId: credential.user)
case .failure(let error):
shouldShowAlert = true
alertTitle = "Error"
alertMessage = error.localizedDescription
}
}
//store the user information in UserDefaults
func saveUserData(name: String?, email: String?, userId: String?){
UserDefaults.standard.setValue(name, forKey: "name")
UserDefaults.standard.setValue(email, forKey: "email")
UserDefaults.standard.setValue(userId, forKey: "userId")
}
//store nil for all user information in USerDefaults
func deleteUserData(){
UserDefaults.standard.setValue(nil, forKey: "name")
UserDefaults.standard.setValue(nil, forKey: "email")
UserDefaults.standard.setValue(nil, forKey: "userId")
}
//this method gets call when the credential revoked notification has been arised in NotificationCenter
@objc func getAuthorizationState() {
let provider = ASAuthorizationAppleIDProvider()
if let userId = UserDefaults.standard.value(forKey: "userId") as? String {
provider.getCredentialState(forUserID: userId) { [self] (state, error) in
switch state {
case .authorized:
// Credential are still valid
break
case .revoked:
//Credential is revoked. It is similar to Logout. Show login screen.
self.deleteUserData()
break
case .notFound:
//Credential was not found. Show login screen.
self.deleteUserData()
break
case .transferred:
//The app is transfeered from one development team to another development team. You need to login again so show login screen.
self.deleteUserData()
break
default:
break
}
}
}
}
}Resources
https://developer.apple.com/sign-in-with-apple/
https://support.apple.com/en-in/HT210318
Conclusion
Sign in with Apple is more secure and easy to implement in any SwiftUI app. I hope that you like this article and also understood how to implement it by following MVVM architecture. If you have any questions consider following me on X and DM me your questions. If you enjoyed this article and would like to support me, Buy me a coffee.
Thank you for reading! 😀 Stay safe and take care!